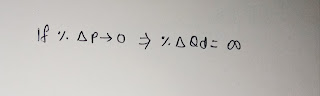Types of Price Elasticity of Demand
There are five types of price elasticity of demand, which are as follows:
I) Perfectly Elastic Demand
If the negligible change in price of a commodity leads to infinite change in its quantity demanded, then it is called perfectly elastic demand. Thus,
In this case, the demand curve will be horizontal as shown in the figure below:
In the above figure, quantity demanded increase from Q1 to Q2 at the same price P1, which implies there is negligible change in price.
II) Perfectly Inelastic Demand(Ep=0)
Whatever be the change in the price of a commodity its quantity demanded remains unchanged, this condition is called perfectly inelastic demand. This holds true for neutral goods. Eg. salt, medicine,etc. Thus,
In this case, the demand curve will be vertical as shown in the figure below:
In the above figure, the quantity demanded remains same at Q1 when price increases from P1 to P2.
III) Relatively Elastic Demand(Ep>1):
If the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in its price, then the demand is said to be relatively elastic demand. Thus,
If %∆Qd>%∆P, then Ep>1
I'm this case, the demand curve will be flatter as shown in the figure below:
This holds true for luxury goods. Eh. TV, car, etc. In the above figure, quantity demanded decreasy from Q2 to Q1, with the increase in price from P1 to P2 in such a way that : Q1Q2>P1P2. So that Ep>1
IV) Relatively Inelastic Demand (Ep <1) :
If the percentage change in quantity demand is less than the percentage change in the price of a commodity, then the demand is said to be relatively inelastic demand. This holds true for necessary goods like price, vegetables, clothes, etc.Thus,
If %∆Qd<%∆P, then Ep<1
In this case, the demand curve will be steeper as shown in the figure below:
In the above figure, quantity demanded decreases from Q2 to Q1 with the increase in price from P1 to P2 in such a way that : Q1Q2<P1P2. So that Ep<1.
v) Unitary Elastic Demand ( Ep=1 ):
If the percentage change in quantity demanded is equal to the percentage change in price, then the demand is said to be unitary elastic demand.
Thus,
If %∆Qd=%∆P, then Ep=1
This is known as the case of happy accident in economics. In this case, the demand curve will be neither flatter nor steeper as shown in the figure below:
In the above figure, quantity demanded decreases from Q2 to Q1 with the increase in price from P1 to P2 in such a way that :
Q1Q2=P1P2 . So, that Ep = 1.
CHAPTER 3 PART 3